Headless working
using web browser
The noVNC client application runs inside the container and listens on the TCP port 6901 by default. The port is exposed to the outside world according the port bindings defined by creating the container.
Table of contents
You can access the running container over the network using a web browser, regardless where the container is running - locally on your host computer or on a remote system.
The noVNC client forwards all requests to the VNC server running inside the container, therefore it shares most of the configuration parameters with it:
VNC_PW=headlessVNC_RESOLUTION=1360x768VNC_COL_DEPTH=24VNC_VIEW_ONLY=falseDISPLAY=:1
The VNC parameters are explained here.
There are also two parameters specific to noVNC client:
NOVNC_PORT=6901NOVNC_HEARTBEAT
NOVNC_PORT: The noVNC client inside the container listens on the TCP port ‘6901’.The default password for the noVNC connection is
headless.
NOVNC_HEARTBEAT: The parameterNOVNC_HEARTBEATis only for advanced scenarios and it has no default value. It’s explained in the section Overriding VNC.
The noVNC port 6901 of the container is usually not bound to the same port on the host system. Although it’s possible, it may not work correctly. The port 6901 must be bound to a free TCP port on the host.
You can find or guess some free TCP port yourself or you can let the Docker to do it for you by providing the parameters -P or -p :6901 to the docker run command.
You should be aware, that the TCP port binding happens at the moment of creating the container and that it stays permanent for its whole life. If you want to change it, you have to re-create the container.
Please do not confuse the container user password with the noVNC connection password. These are two different passwords, even if they both have the same default value of ‘headless’.
Exercise
Let’s say that you want to create a container, that will not keep running in the background, but removes itself after the exercise is completed. You want to access the container using a web browser on the TCP port
36901.
The TCP ports in this range are usually free, but it can happen, that the port
36901is not. Then you need to use some other free TCP port.
Open a new terminal window on your host and execute the following command:
docker run --rm -p "36901:6901" accetto/ubuntu-vnc-xfce-g3
Parameter
--rmcauses the automatic container removal after it is stopped.Parameter
-p "36901:5901"binds the noTCP port6901of the container to the TCP port36901of the host computer.Note that the container is running in the default foreground mode because the parameter
-d(detached) has not been provided.
Assuming that you’ve created the container on your local host computer, you can access it by navigating your web browser to the following URL:
http://localhost:36901
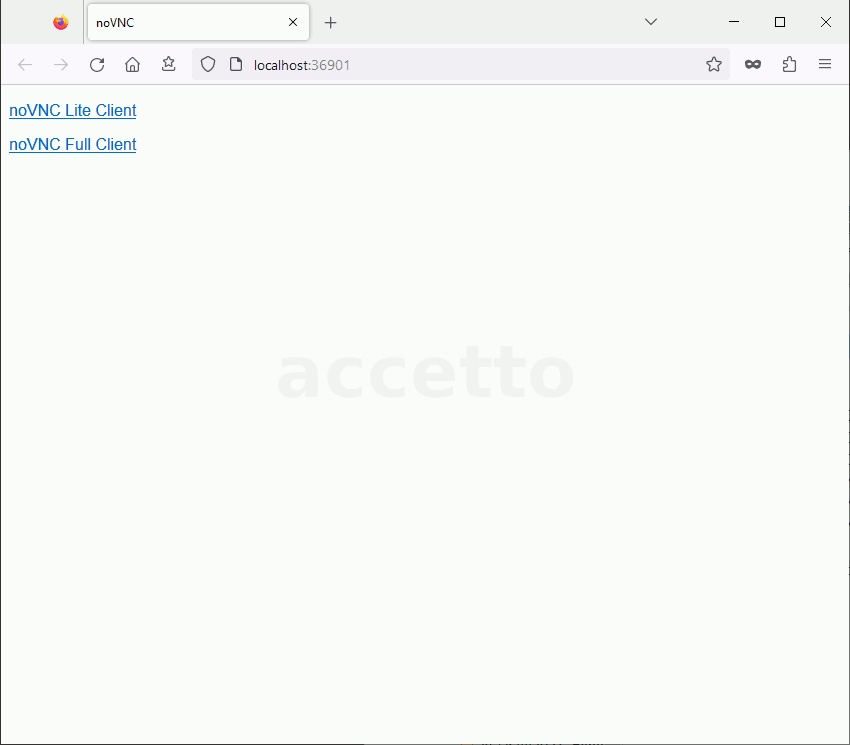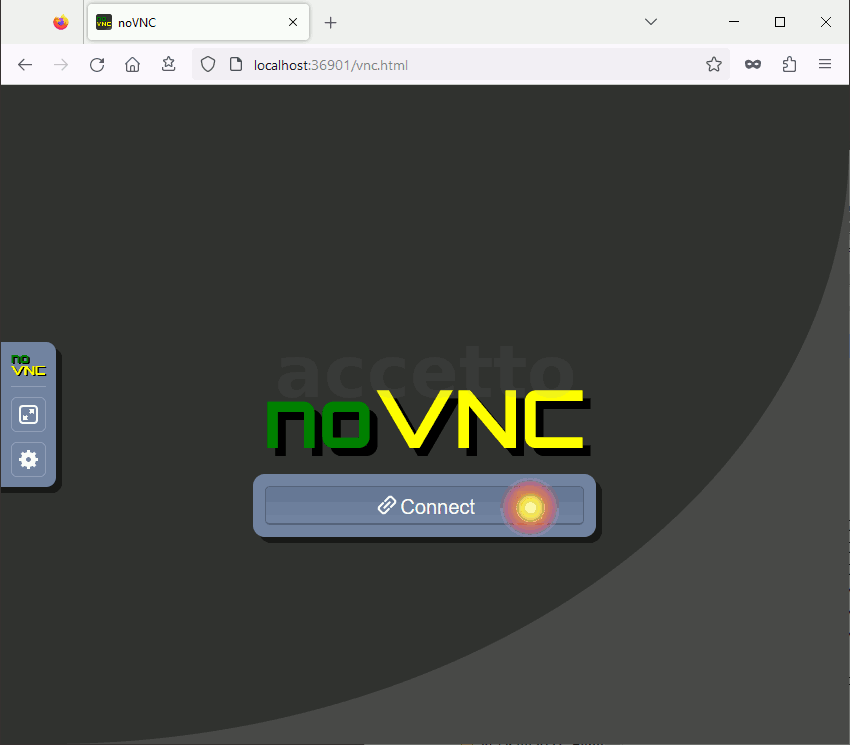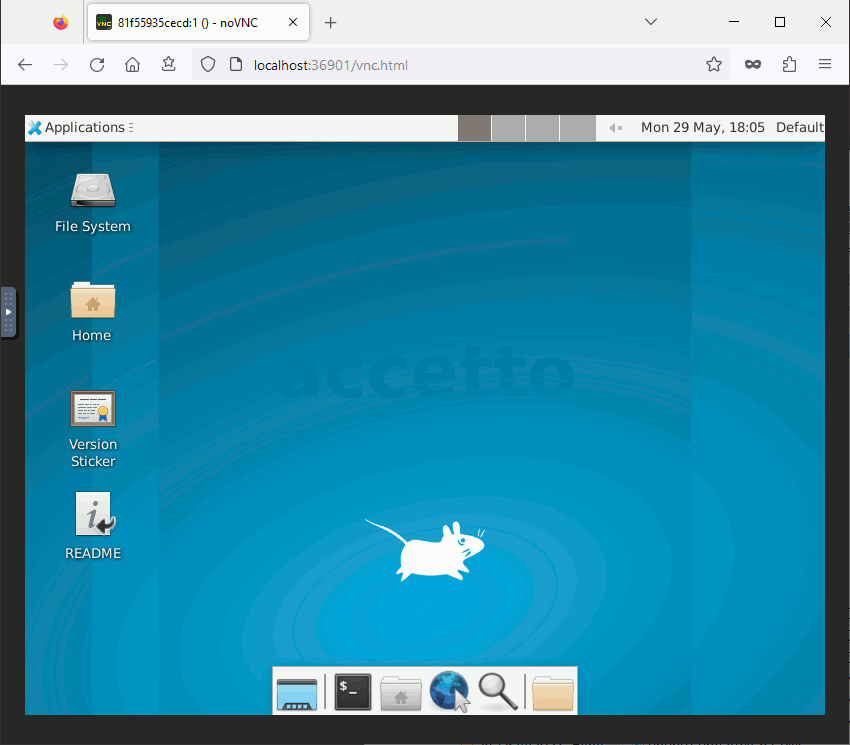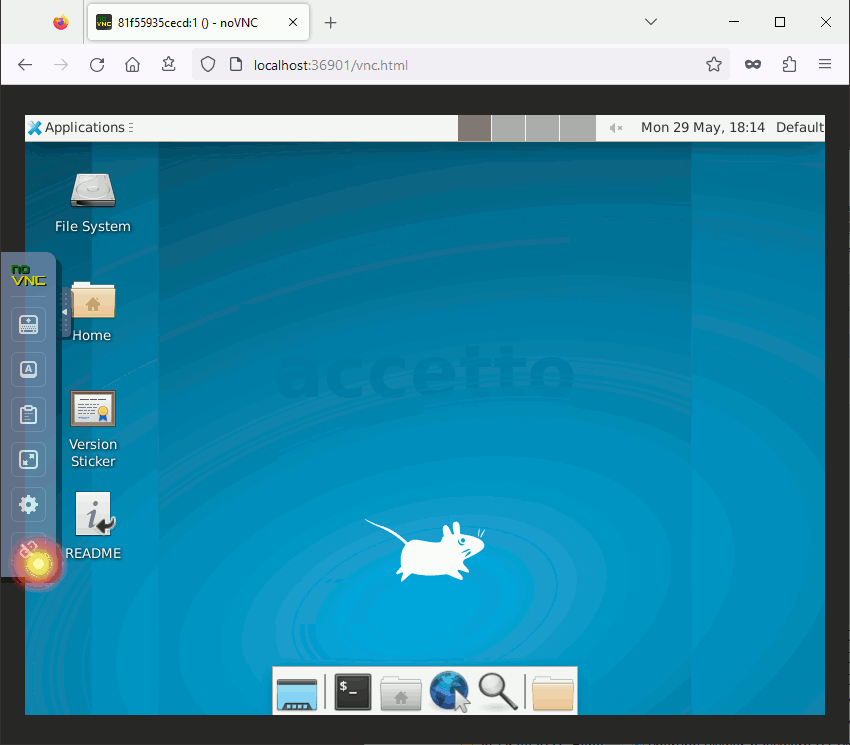
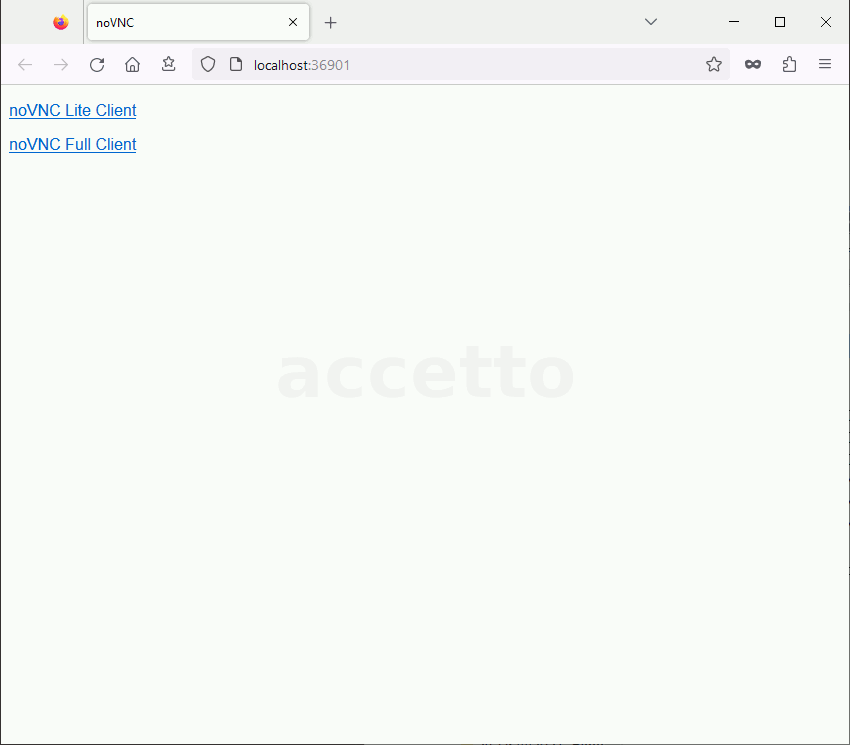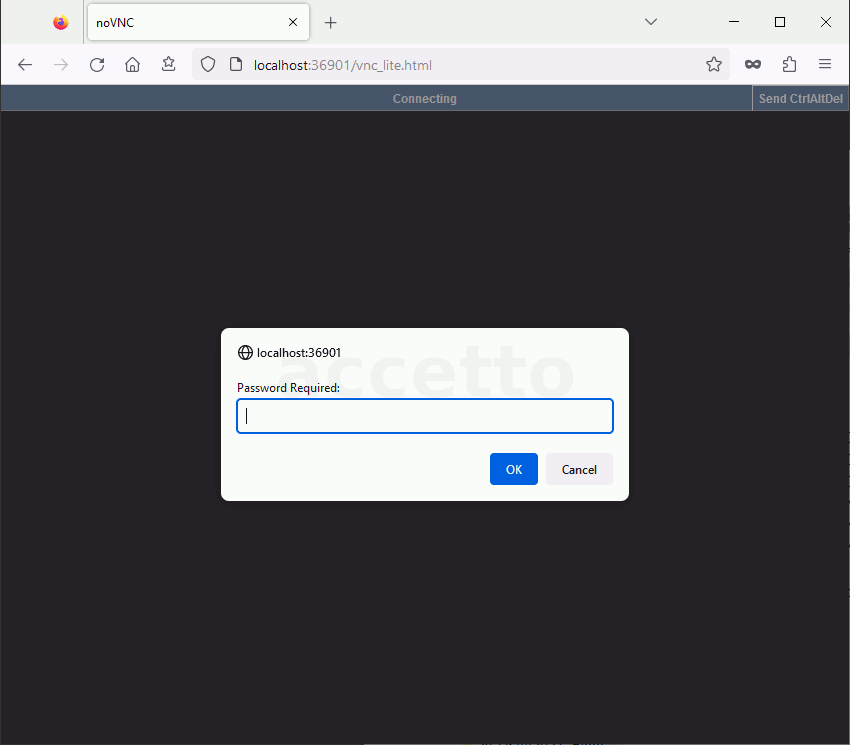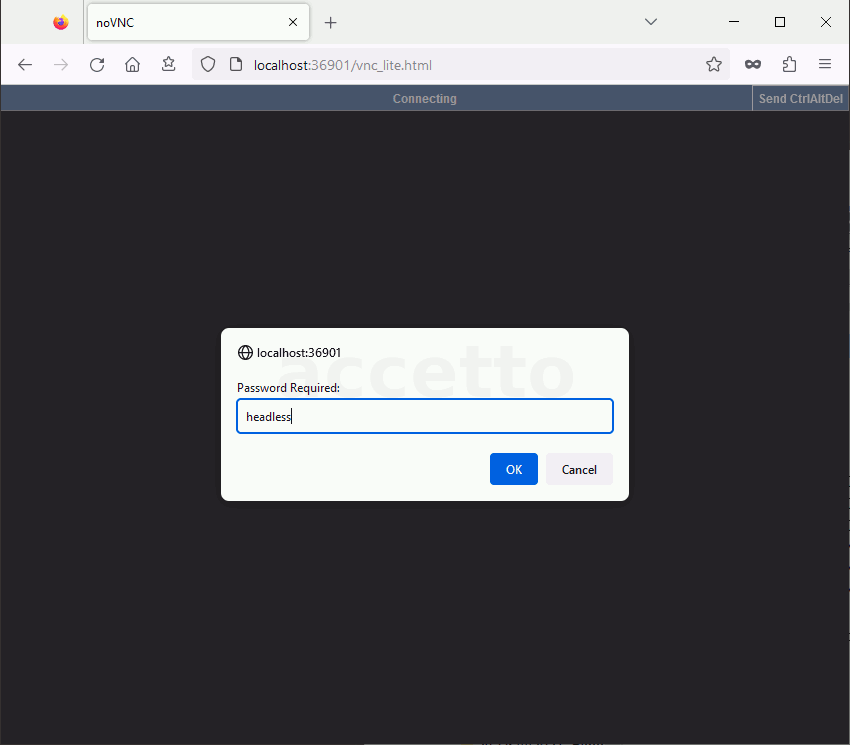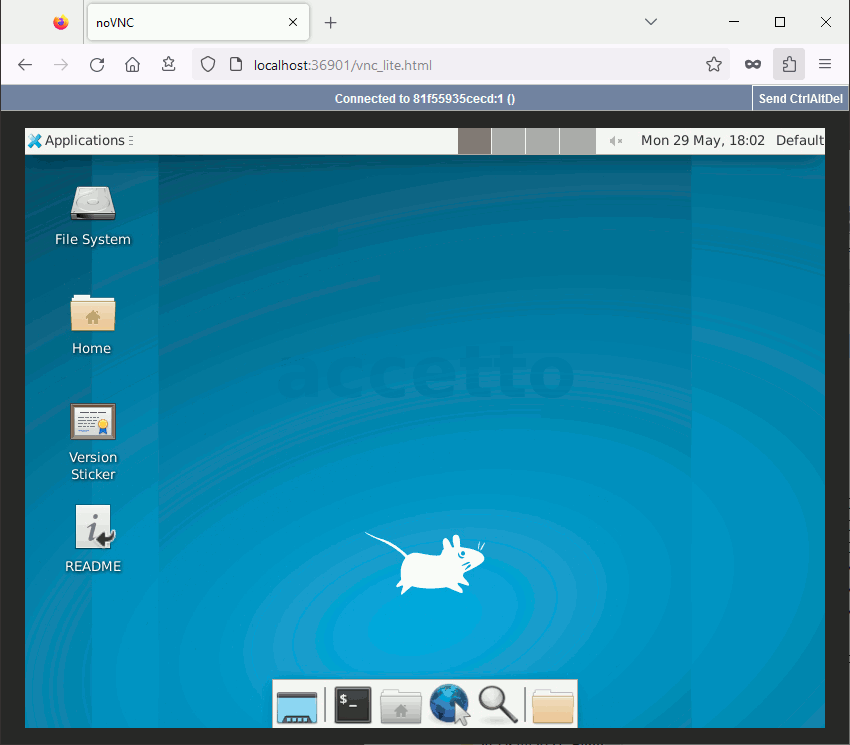
All accetto containers actually include two noVNC clients - the lite one and the full one.
The container displays a simple starting page containing the links to each client:
- noVNC Lite Client (
http://localhost:36901/vnc_lite.html) - noVNC Full Client (
http://localhost:36901/vnc.html)
It is also possible to provide the connection password through the links.
For example:
http://localhost:36901/vnc_lite.html?password=headlesshttp://localhost:36901/vnc.html?password=headless
The following animations illustrates the connection process. Input ‘headless’ as the password in both cases.
Lite client
Full client